The “Search” process, which is an essential component of operating systems such as Windows, is critical in quickly locating files and information.
This feature allows users to quickly locate files, applications, and settings throughout their system. The search procedure enhances data retrieval by utilizing indexing services, making it a vital tool for those seeking rapid and convenient access to their files.
Despite its importance, the Search process occasionally meets issues that appear as excessive CPU/GPU consumption in the Task Manager.
What causes the Search process to use excessive CPU/GPU?
The Search process’s sudden increase in CPU/GPU consumption can be attributable to a variety of factors. One obvious cause is the indexing of massive amounts of data.
Because the system regularly updates and maintains a file index, a big database might put a burden on the hardware, resulting in increased resource consumption.
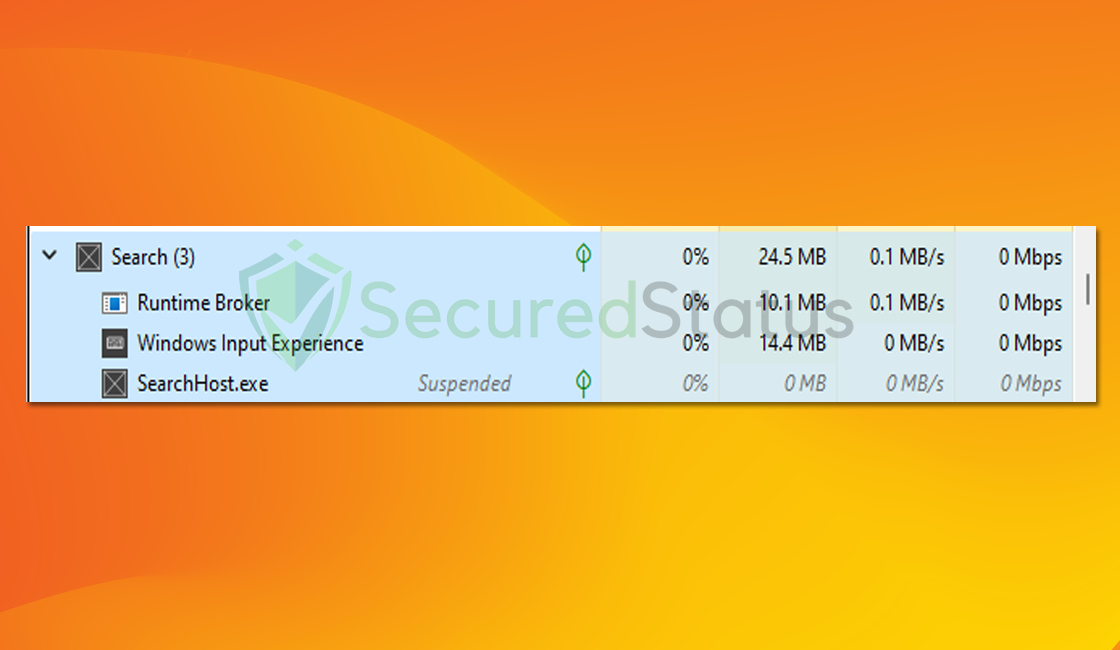
Inefficient search engines or poorly tuned system updates may also contribute to this problem. The possible infection of the Search process is an often neglected yet crucial factor.
Malicious individuals may compromise the system by exploiting flaws in the search capability. A compromised search process may run dangerous scripts or actions in some situations, resulting in a large rise in CPU/GPU consumption.
Users must be cautious since an infected search process can cause system instability and expose sensitive data.
Aside from viruses that directly target the search process, another risky situation involves malware masquerading as a legitimate search component.
Malicious software can imitate the behavior of the search process, fooling both users and the system. This disguised virus consumes a large amount of system resources while deliberately avoiding detection.
If you are experiencing the negative consequences of high CPU/GPU consumption as a result of the Search process, there are steps you may take to solve the problem. Please follow the instructions below to prevent the Search process from consuming too much computer hardware.
Fix Search process consuming excessive CPU/GPU
The methods provided below will assist you in removing any potential malware, trojans, rootkits, and viruses from the computer system, and fix errors in the computer system that may have resulted in this issue.
Removing malware from the system and the browser should be thorough and carefully executed; therefore, please follow every step provided. We’ve verified that the provided steps are current and effective.
We made the instructions below easy to understand so non-tech-savvy users can still remove the browser threat without needing help from tech support or a computer technician.
Please inform us using our Contact Page if you come across a method that does not appear to be working. We value the feedback you provide and will address the issue as soon as possible.
Step 1: Utilize System File Checker and DISM Cleanup
DISM Cleanup and the command-line tool Windows System file checker can be used to verify the stability of all significant system files. Additionally, it checks to determine whether any system files are missing or corrupted by comparing them to their original versions.
If the Search process was tampered by malware, following this step will fix it.
1. Click the Windows Button from the keyboard and search for CMD or Command Prompt.
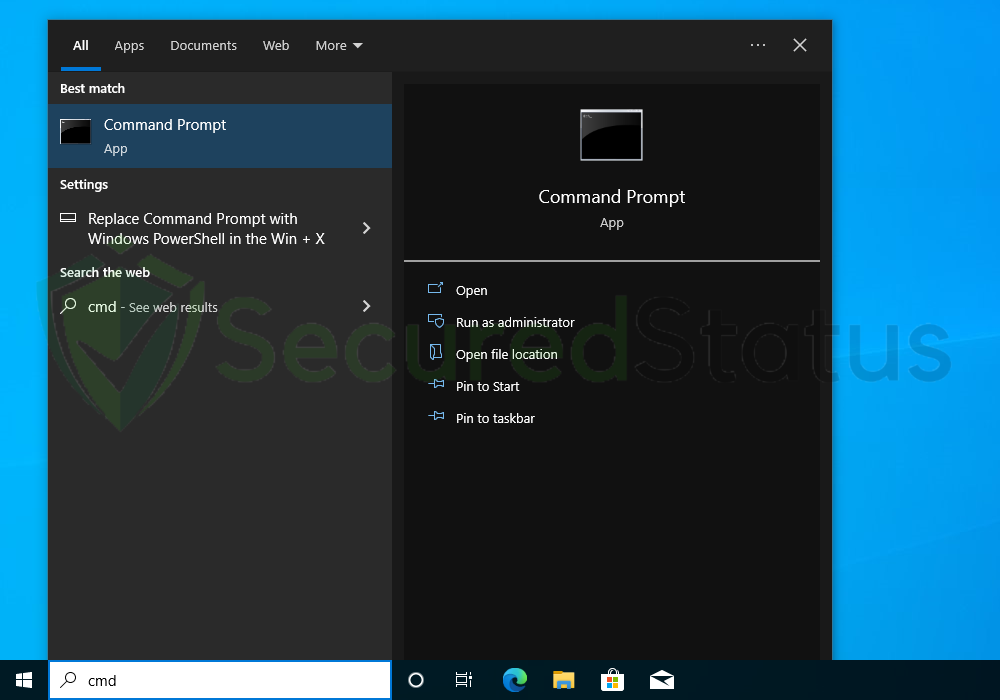
2. Right-click the Command Prompt application and select Run as administrator.
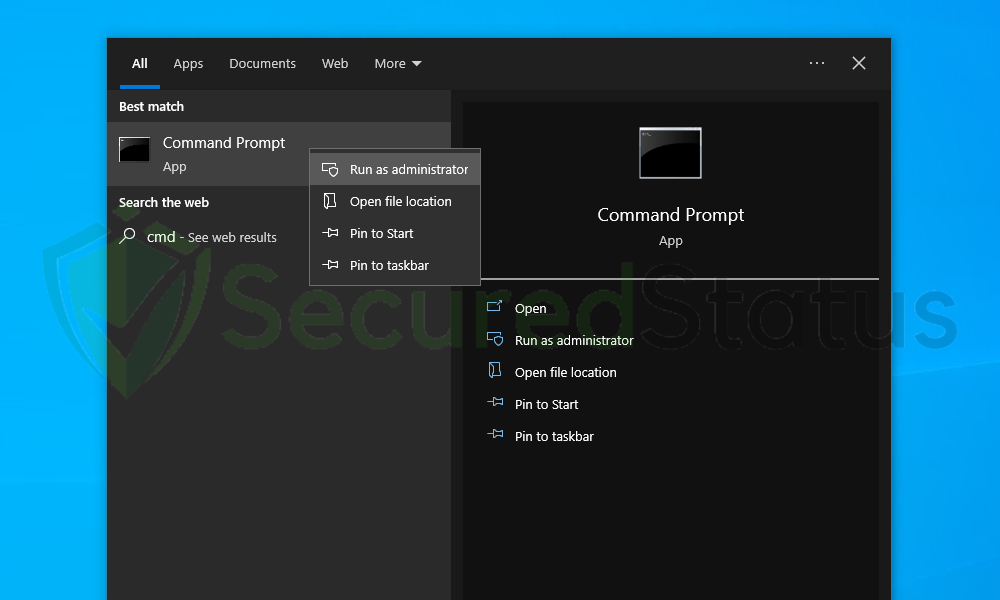
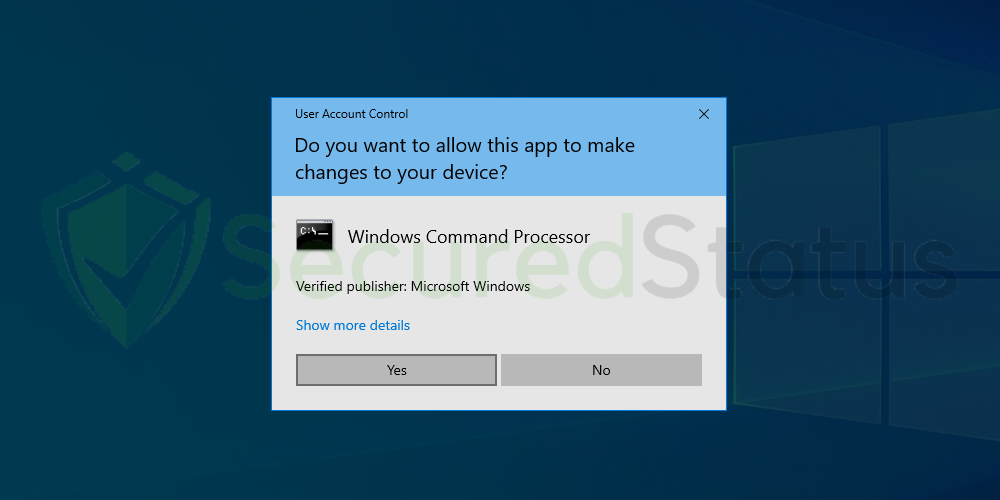
3. The User Account Control confirmation message will pop up, click Yes to proceed.
4. Once the Command Prompt opens, type sfc /scannow and hit enter. Please be patient for a few minutes as the scan will start and could take some time.
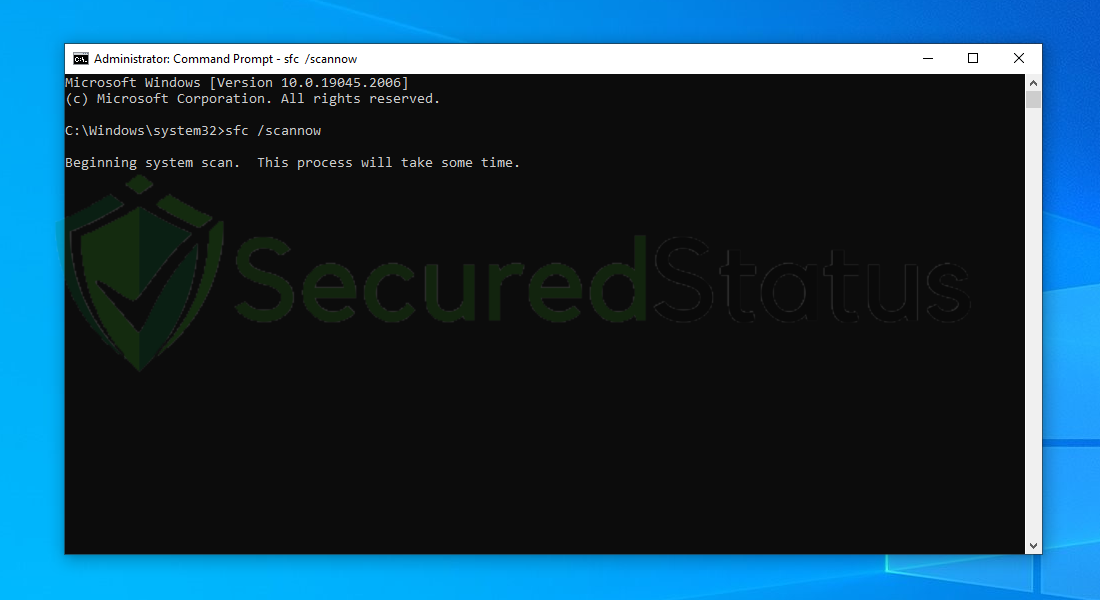
5. After the scanning process it will report that it has successfully found corrupt files and has repaired them.
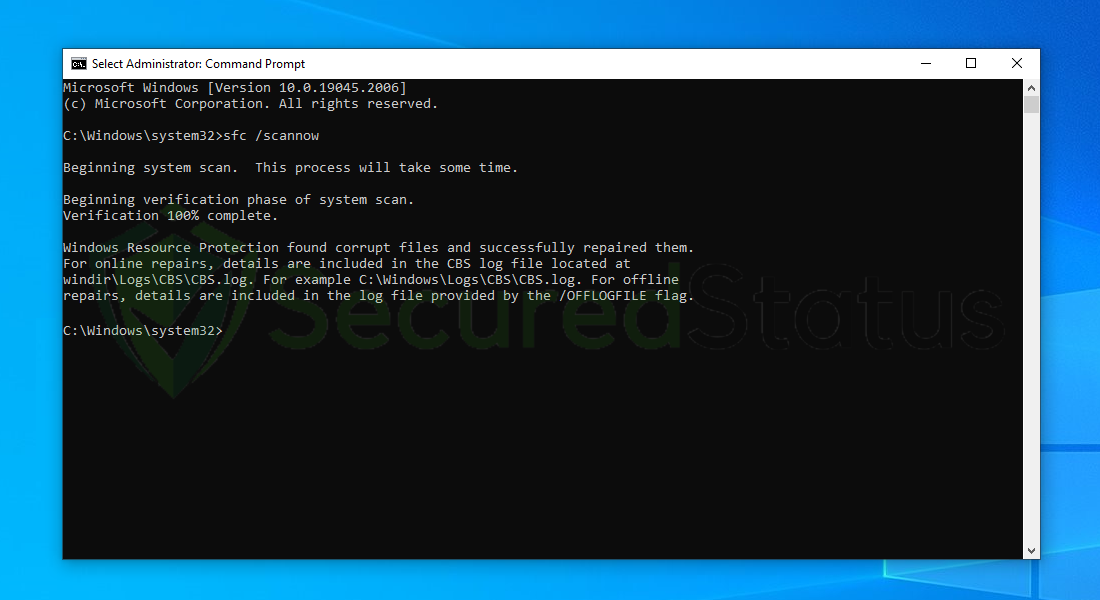
6. Next is to use the DISM Cleanup to patch faulty files in the computer system. Type dism /online /cleanup-image /scanhealth onto the command line and hit enter. Wait for a few minutes while it is scanning.
7. After the scan is complete, it will report that the operation is successful and that all corrupted components will be fixed.
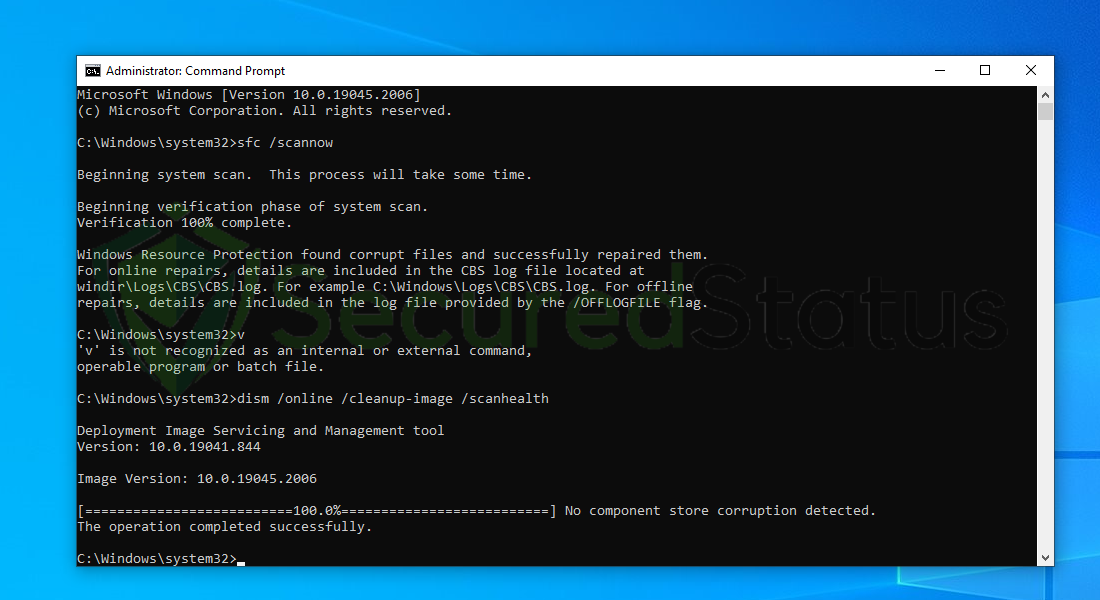
8. Lastly, in order to fix serious windows errors, we will use the restore health command. Type dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth and hit enter once again to start the scanning process.
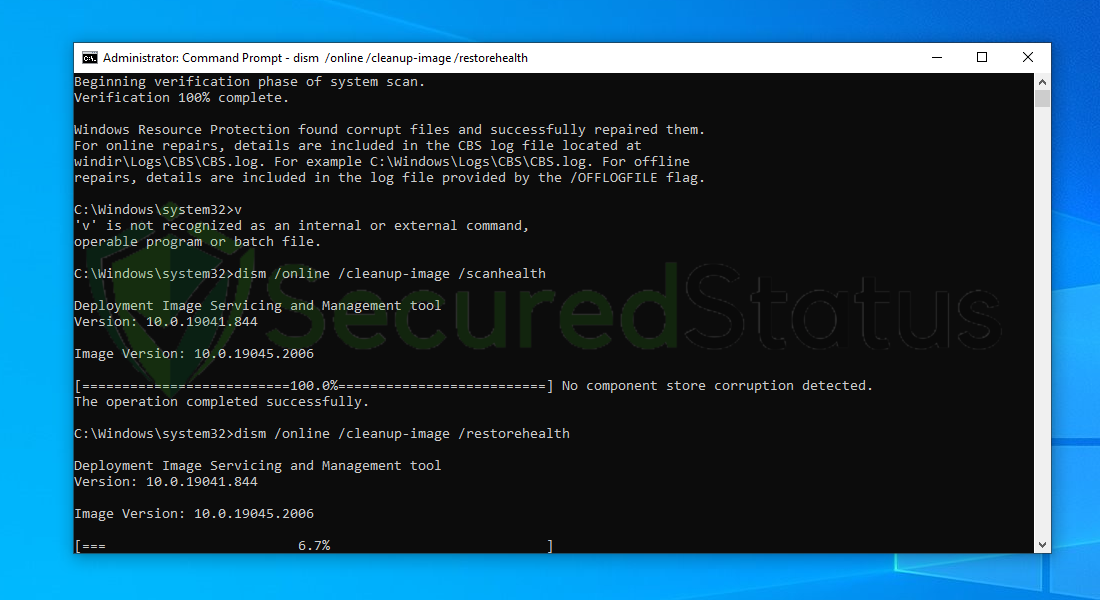
9. Once the scan is complete, it will report that the operation was successful and corrupted files and entries are resolved.
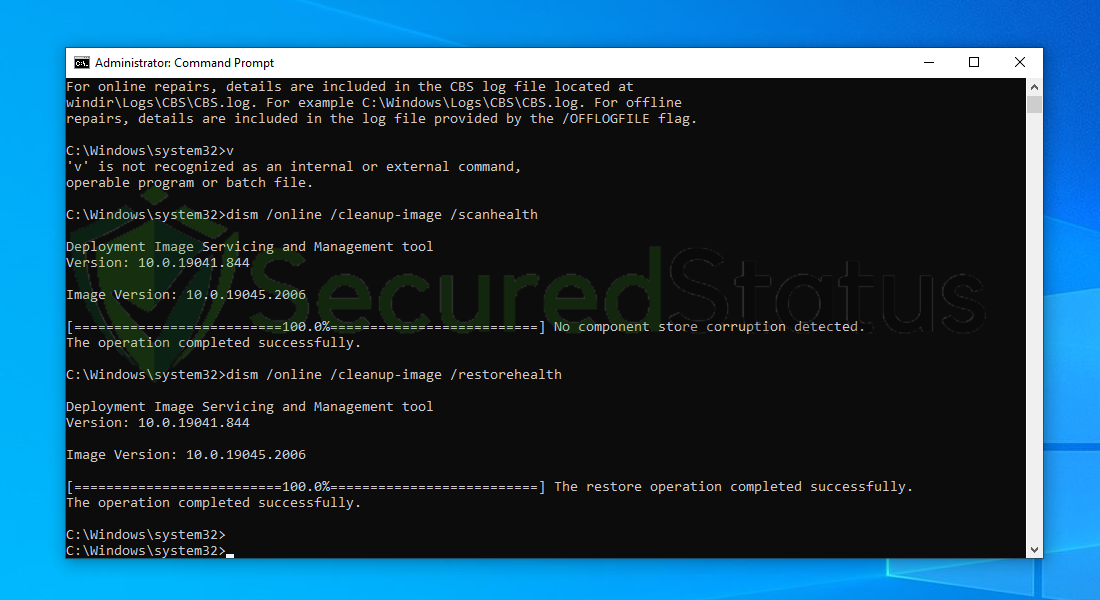
After following the instructions, restart your computer and see to it that the Search process is still utilizing a great amount of computer hardware.
If the issue still persists, then it shows that the Search process is not a system process but a malware disguising under it’s name.
Step 2: Scan with powerful malware removal software
The Search process is malware hiding in disguise therefore it is crucial to remove it. They can also conceal themselves within the system files and registry, making them resistant to browser reset and software uninstallation.
Finding the location of the Search process can be easy, however removing it can be quite difficult when done manually, this is why it is much easier to remove it with a single click by utilizing an antivirus software.
An antivirus application is a one-stop shop for dealing with malware and potentially unsafe websites. It acts as both a preventative and corrective measure, immediately detecting and removing malware from your device.
We cannot overstate the importance of utilizing antivirus software when facing threats such as the Search process malware in disguise.
Furthermore, any malware that may have been installed on your computer unwittingly will be intercepted, and any downloads will be stopped as soon as they begin.
Having antivirus software on your computer offers several significant benefits, including:
- Detection, filtering, and automatic removal of malware ranging from harmless adware to extremely severe ransomware.
- Providing caution and notifications for possibly risky websites that you may visit, helping you in mitigating online risks.
- Antivirus threat databases are regularly updated to ensure the detection of new viruses and the protection of your device.
- Keeping your operating system clean by protecting all files on your computer, assuring their safety and integrity.
But which antivirus should I use?
The answer is based on how you use your computer, as several antivirus software on the market have advantages and disadvantages. Because the majority of them detect and remove malware at the same rate, we recommend making your selection based on research.
For example, if you use your computer for resource-intensive tasks like video editing, you may wish to avoid resource-hogging antivirus software.
Fortunately, various reviews provide detailed comparisons of each antivirus’s advantages and disadvantages. However, for the best of all worlds, we recommend one of the antivirus applications listed below:
The majority of free versions are already sufficient for removing and blocking viruses from your computer. Some antivirus products also provide free trials that allow you to learn more about their capabilities before making a purchase choice. However, in the end, the free version usually provides everything needed to remove malware.
For a better and safer web browsing experience, we’ve provided a few security measures and advice below that will safeguard your browser and computer from harmful threats like worms, malware, trojans, keyloggers, stealers, and other kinds of computer viruses that will harm user data.
Protective measures for better overall security
Removing trojan viruses and malware from the device is one thing; keeping it secure for the future and for a long period is a different thing and will require certain things to make sure you are secured, especially if you do not know most of the ins and outs of the device you are using.
Cybercriminals are always stepping up their game to make sure they infect users and extract data and money from them.
We encourage you to take the actions listed below to ensure complete security before leaving this page because we strongly promote web security and having a secure online presence.
Safeguard your data and privacy online by using a VPN application
VPNs, also known as virtual private networks, guarantee your safety and complete anonymity while you browse the internet.
In contrast to a firewall, which monitors and blocks potentially harmful connections in the network, A VPN hides the user’s connection via a tunnel so that it would appear to third parties as a different IP address and location.
This ensures that your data won’t be leaked because the program hides it. Be aware that visiting infected websites may cause your IP address and location to be disclosed; however, if you use a VPN, this will prevent your true IP address from being revealed to malware actors.
Utilize an adblocker when browsing the internet
Installing an adblocker on the browser is the best way to prevent hijacker viruses such as $$custom_field:vname$$ as well as other threats such as pop-ups, redirects, and unwanted toolbars.
Additionally, by blocking malicious websites before users can even access them, it is possible to prevent malware from being downloaded.
In this case, we recommend uBlock Origin, which is an open-source AdBlock extension that comes at no cost and is free forever. It is one of the most reliable plugins out there, ensuring that every advertisement on a webpage will be blocked.
The majority of pop-up advertisements, whether they include malware or not, will be filtered by the extension and no longer be displayed to you. Currently, uBlock Origin is not available for Mac or iOS users, but there are plenty of free options on the market, such as AdBlock for Safari.
Use a firewall to prevent cyber attacks
A security firewall is required for every internet connection that is made. It is an essential tool that enhances security and stops online attacks.
Through a security mechanism, it controls incoming and outgoing network connections on your system and network and filters the undesirable ones. Consider it a further barrier against malicious assaults and zero-day exploits.

