What are Malware and Viruses on Mac OS
If you experience unusual activity from your Mac, such as pop-up advertisements and website redirections, your device might have been infected with malware.
Despite having excellent safety features, Macs are nevertheless vulnerable to malware and virus attacks. It can take several different forms and harm your device in various ways.
How does the Mac OS become infected?
If you’re wondering how malware infiltrates the Mac OS, below are a few ways how it approaches users. Take notice of these methods to prevent a malware infection on your device.
Numerous users unwittingly download viruses into their devices every day, so it’s advised that you share the information with everyone you know regarding how it attacks devices to prevent additional problems.
Pop-up advertisements
Pop-up advertisements are one of the ways that adware can be downloaded and installed on a user’s computer. Cybercriminals prefer this approach since it’s quite likely that someone browsing online may unintentionally click it.
Adware developers use it to entice users. Furthermore, the use of pop-up advertisements is a common method used by hackers to insert harmful malware onto your device.
Fake Alert Downloads
Fake alert downloads are a common way for malware to get installed on a system. Even if you don’t interact with the website, the virus can still be automatically downloaded. Since it is so deceptive, many unaware users might fall for it.
This frequently happens on websites that have been compromised and websites run by cyber criminals. People need to exercise caution when browsing the web to prevent visiting these kinds of sites that may damage their devices.
How do cybercriminals utilize malware on Mac?
By placing adverts on the user’s computer, cybercriminals make money. Adware may have been developed by someone other than the advertisers, and it only displays the advertisements that the advertisers desired the users to see.
It is also used by hackers to gain control over a user’s browser. They use this to lead individuals to specific websites without their authorization, and to websites that display unwanted advertisements.
Furthermore, it redirects users to websites that collect data about users. They can also keep tabs on an individual’s surfing habits and preferences, using this data to determine the kinds of advertisements that will be displayed to the user.
They can make money not only from the adverts but also from other methods, like data collection and browser customizations that benefit the people who paid the cybercriminals. Additionally, they also earn by having to install dangerous programs other than adware.
Mac Adware & AdLoad
Adware, also known as advertisement-supported software is used by cybercriminals to show advertisements to user’s computers.
These types of applications have the icon of a magnifying glass which makes them easier to identify. It can be very annoying for users since they’ll be bombarded with advertisements evetime they open the browser.
It will display unwanted content such as advertisements and can also function as spyware, gathering information from the infected user that will eventually be sold to advertisement companies.
Whenever a user opens their browser, adware shows them one or more suspicious and potentially harmful adverts.
Adware commonly gets installed on a user’s device when they download from third-party programs and do not uncheck the installation option for additional programs.
It generates money for its developers by displaying unwanted advertisements. Additionally, third-party advertising companies often purchase user data that has been tracked and stolen.
| Recently Found Mac Adware |
|---|
Browser Hijackers
Numerous browser hijackers target Mac users especially. This malware can gain access to the web browser causing it to perform unpredictable and odd actions.
After installation, it will modify the web application settings, search engine selections, and homepage tab. Furthermore, this kind of malware could redirect your browser to unwanted websites and interfere with search engine results.
Browser hijackers should be uninstalled as quickly as possible since they allow third-party advertising to gain access to users’ browsing habits. This information may be used for marketing purposes, which might harm your computer by downloading malicious programs or other software.
If you have been infected with a browser hijacker, different pop-up advertisements will appear every few minutes. It may be displayed through the websites you visit, search engines, or notifications. Furthermore, you may be redirected to unwanted websites every time you browse the internet.
| Recently Found Browser Hijacker Threats |
|---|
As soon as it is installed on the Mac OS, it will immediately begin to show advertisements in notifications and on all visited websites. The advertisements may not always be helpful or relevant, and they could potentially infiltrate open web pages in the browser and start displaying ads there.
In addition to hurting your web browsing experience and privacy, this malware program may also hinder the performance of your system and interfere with online security tools like antivirus software.
How to Remove Malware & Viruses From Mac OS
This procedure will assist you in removing malware and viruses from your Mac computer. You can rest assured that the information provided below has been tried and tested.
Step 1: Remove Malware and Associated Files
The first step is to address the source of the problem, which is removing the malware from the system. Since this sort of malware takes the form of an application, it can be removed easily with only a few clicks. It’s also worth noting that leftovers and files related to the malware should be deleted as well.
Remove Malware from Applications
1 Open the Finder application from the Dock.

2 Select Applications from the left sidebar.

3 Find the suspicious malware then right-click its icon then select Move to trash. (We will be using the MacKeeper application as an example.)

Remove Files Associated with Malware
1 Click the Go from the Finder toolbar and select Go to the folder from the expanded menu.

2 Search the following paths for files associated with the malware. These files will have the .plist extension and will look similar to com.alphaconsole.plist. (Note: Do not delete files that come from legit applications)

~/Library/LaunchAgents
~/Library/Application
/Library/LaunchAgents
/Library/LaunchDaemons
3 Once you have found them, right-click and select Move to Trash to get rid of those files.

Empty the Trash Bin
1 From the Dock, right-click the Trash application and select Empty Trash to delete the files permanently.

2 A confirmation window may appear asking if you want to delete the files on the Trash, go ahead and proceed to delete them.

Now, the application as well as files related to the malware threat are permanently deleted from the Mac system.
Step 2: Remove Profiles Created by the Malware
Malware can prevent users from reverting to their default browser settings. As a result, when users attempted to alter their preferences back, they were either unable to do so or their preferences were turned back after a few minutes.
Removing the profiles added by malware is required to ensure that configurations are not altered again once they have been reverted. (Note: If the device does not have any profiles related to the malware, you may proceed to the next step.)
1 Click the Apple logo on the upper left corner of the screen then select System Preferences from the drop-down menu.

2 On the System Preferences window, find and click Profiles. (If you cannot find Profiles, then it means you do not have profiles on your Mac. You may skip this procedure and head over to the next step.)

3 Find and remove profiles that may be associated with the malware. Click the minus button on the lower left part of the window to remove the profile.

Step 3: Reset the Infected Browser
Your browsing program is most likely tainted by malware since this type of malware relies solely on the usage of internet content which is why resetting it will undo the changes done by the malware.
If you do not wish to reset your browser, you can undo the changes manually by removing the extension and changing the default homepage and search preferences back to normal. However, if you are not much of a techy person, resetting the browser will be the easier approach.
For Google Chrome: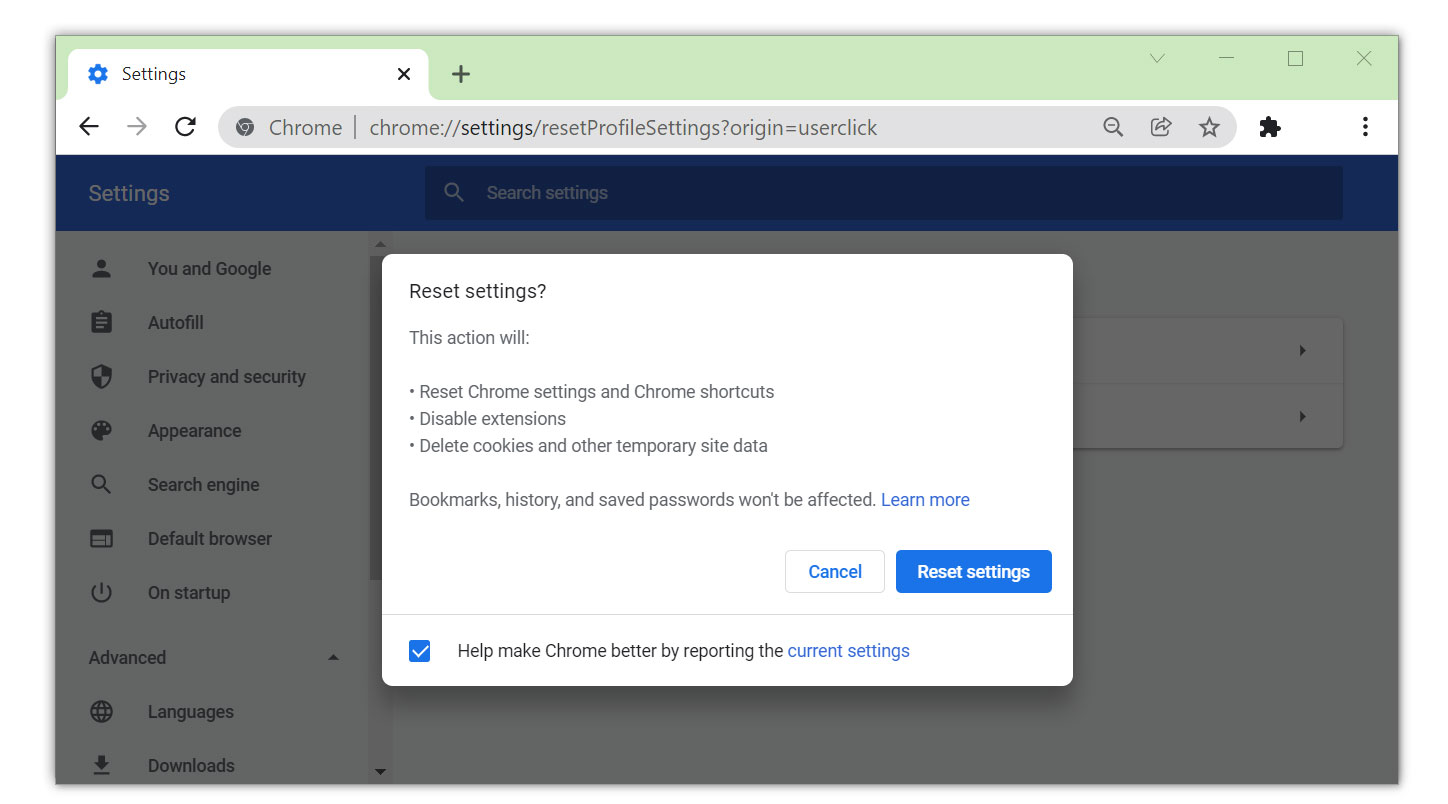
1 Open Google Chrome and click the three dots in the upper right corner of your screen to access the Google Chrome menu.
2 Click the Settings button, then click the Advanced menu on the left side of the screen from the settings screen.
3 On the drop-down menu, select Reset settings.
4 Click on the Restore settings to their original defaults.
5 When a small window will appear and click the Reset Settings.
For Safari:
We will be using the utilization of the Terminal application to reset the Safari browser because, unlike Chrome or Firefox, it does not have an auto-reset feature for the browser.
1 To use the Terminal application, open Finder and navigate to the Applications/Utilities folder.

2 Copy and paste each code line separately in the Terminal. Some of the first codes will have a confirmation line, type y to continue. (Note: Make sure the Safari application is closed while proceeding with working with the codes.)

rm -Rf ~/Library/Cookies/*;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Cache/*;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Safari/*;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Caches/Apple\ -\ Safari\ -\ Safari\ Extensions\ Gallery;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Caches/Metadata/Safari;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Caches/com.apple.Safari;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Caches/com.apple.WebKit.PluginProcess;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Cookies/Cookies.binarycookies;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/Apple\ -\ Safari\ -\ Safari\ Extensions\ Gallery;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Safari.LSSharedFileList.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Safari.RSS.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.Safari.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.WebFoundation.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.WebKit.PluginHost.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Preferences/com.apple.WebKit.PluginProcess.plist;
rm -Rf ~/Library/PubSub/Database;
rm -Rf ~/Library/Saved\ Application\ State/com.apple.Safari.savedState;
After running all the codes to the Terminal application, the Safari browser should look good as new.
For Mozilla Firefox:
1 Launch Mozilla Firefox browser then open the menu by clicking on the three horizontal lines located in the upper right corner.
2 Navigate down and click Help then select More Troubleshooting Information from the options given.
3 Select the Refresh Firefox button.
4 A confirmation window will appear, click Refresh Firefox.
Step 4: Scan with Malwarebytes Anti-Malware
Malwarebytes Anti-Malware is one of the most powerful anti-malware programs available for the Mac OS. They have some of the most advanced threat detection tools, ensuring that any harmful virus on your computer is eliminated.
1 Using your web browser, go to the official anti-malware website or click the button above to download the most recent version of the program. When you first download the application, you will also receive a 14-day trial of the premium software.

2 After the file has finished downloading, click on the installation package and run the file to start installing the application.

3 Follow the installation procedure shown on the setup and wait for it to finish.
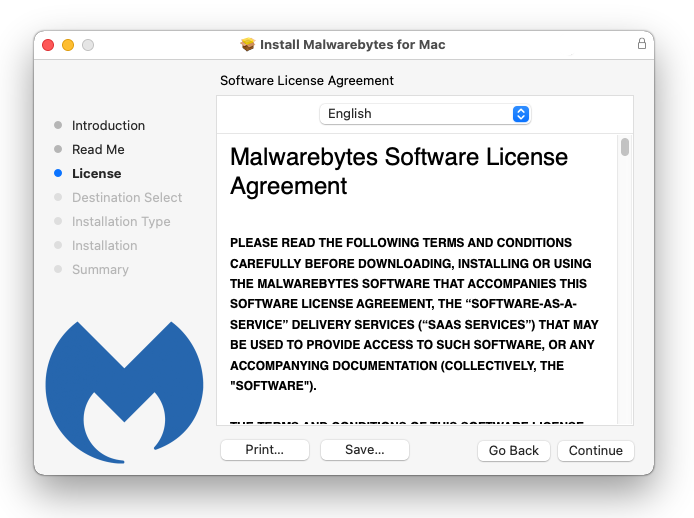
4 Your password may be required to continue installer from installing the new software. Permit it and click Install Software.
5 Wait for Malwarebytes Anti-malware to finish installing on the Mac system.
6 Once the process is complete, the application will open. Click on the Get Started button and follow the procedure to start using Malwarebytes.

7 When prompted to choose between personal and organizational use, click the personal option unless you are downloading it within your company.

8 After the initial start-up, proceed to run your first scan. The scanning may take a while depending on how many files you have on your system.
9 Malwarebytes will show all malware identified on the machine after the scan, and you can remove the detected threats by pressing the quarantine button. (Note: Some threats may require a restart of the computer.)

The malware, as well as any other potential threats identified on the Mac system, should be removed once the process is finished. We also recommend turning on Malwarebytes Real-Time Protection, which will secure your computer and detect threats as soon as they appear.
Tips to be safe online
- It is preferable to avoid websites with unique domain extensions other than .com, .org, .net, and.edu. Because most infected websites have extremely distinct TLDs, always verify the last part of a domain to ensure that you are visiting a safe site, unless the site has been reputable ever since.
- Never acquire software or programs from unknown sources, as this is one of the most common ways for malware and other types of viruses to attack your computer. Only download from reputable and legitimate websites. To be safe, stay away from torrent downloads and cracked software download sites, as there will always be malware in the files.
- Using a firewall is one of the most foolproof ways to be safe online. It serves as a first line of defense against dangerous websites, shielding visitors from potential risks. It protects the user’s network and device from intruders. A firewall will safeguard a user from the threats hiding on the vast internet in today’s age.
- It is essential to keep anti-virus software up to date on a computer since hundreds of new malware threats are released every day that target the machine’s vulnerabilities to infect it. Anti-virus updates include the most recent files required to counter new threats and safeguard your machine.
- Only visit websites that have a secured connection. A site with an HTTP connection does not encrypt the data it receives and therefore is not considered secure. Entering personal information such as email addresses, phone numbers, and passwords on a website with an HTTP connection is risky since it could be compromised and your information was stolen. Websites with HTTPS connections, on the other hand, are secure since data is encrypted and attackers are unlikely to gain access to information exchanged within the site.

